Semantic Web Advantages
What is Semantic Web
In the year 2001, Lee Feigenbaum et al had laid the theoretical foundation of Semantic Web by demonstrating the possibilities of the World Wide Web maturing into a highly interconnected network of data that could be accessed and understood by PC or handheld device. It had meant the beginning of an era which one day would ultimately signal a good bye to inputting multiple search terms and sorting through endless pouring results and culminate into the application of intuitive software agents that would handle multiple jobs on a single customized question.
See also: The Differences Between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
Semantic Web Advantages: Predictions and Actions
Subsequent practitioners of Semantic Web have also been making possible of their predictions and actions in a variety of ways. For instance, with the application of Semantic Web technologies, it is possible to automate operations, say, from completing all that you need for a travel to updating of your personal records. Semantic Web then can be defined as a web of information on the Internet and Intranet that contains characteristics of annotation which enables accessing of precise information that you need.
Semantic Web in action has been conferring advantages in an ongoing basis and in initial stages had proved beneficial in sophisticated operations as logistics planning in military operations. The US military was the first one to adopt it; however it has been extending such benefits to other applications also some of which are presented below:
Health Care and Life Sciences
In Health Care and Life Sciences its application is advantageous because these disciplines have to deal with data from multiple sources, which have multiple applications and there is no completeness in such data.
Engineering Analysis
Semantic Web could be applied to engineering analysis by availing innumerable advantages it offers. Engineering analysis involves handling complicated data sets in countless formats. Semantic Web in particular confers the following advantages to engineering analysis.
- The data would not be lost in the servers
- There is no need for an expensive Product Date Management (PDM) system
- The data could be tailored to return in a uniform manner across the companies
- A variety of checklist analysis could be conducted simultaneously
Data Warehousing
In data warehousing it has specific functional utilities. There is no need for a data base schema; this means you can dispense away the necessity to make a decision about the structure and recording of data; in addition data can be distributed over the Web, because Semantic Web is neutral to data security.
It has cost advantages too for business operations, for the businesses can precisely define the processes suited for them and the system would do exactly what that business specifies and nothing more and nothing less. This makes technology affordable for small businesses also.
Specific Semantic Web Technology
Semantic Web has developed specific Semantic Web Technologies that could be implemented free of cost that could result in huge savings in the way the Web functions. An example of this is SPARQL, a query language
It would however be erroneous to assume that Semantic Web is something that has descended from nowhere to usher in a rethinking in everything. One may be tempted to use such terms as that a revolutionary mind set would be needed to its application etc. or it represents a paradigm shift which are all not correct and would only confuse and mask the real advantages it is offering. It is neither a total replacement nor would it substitute all that has come before it, which would and continue to exist. No doubt, there could be changes, but, these changes would build and bridge the gap by leveraging the existing assets rather than replacing them.
Reference
Tim Berners-Lee, James Hendler & Ora Lassila (2001): The Semantic Web: A new form of Web content that is meaningful to computers would unleash a revolution of new possibilities, Scientific American,
Lee Feigenbaum, Ivan Herman, Tony Hongsermeier, Eric Neurmann & Susie Stephens (2007): The Semantic Web in Action, Scientific American
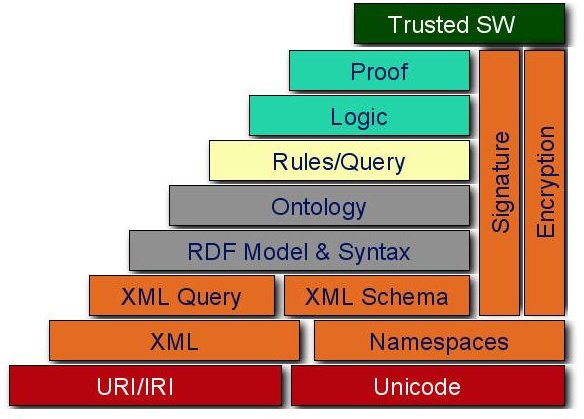
Image Credit: Semantic Web Stack - https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:W3c_semantic_web_stack.jpg