Leptin Resistance and the Danger of High Fructose Corn Syrup
What is Leptin?
Within the human body, leptin operates as a hormone controlling intake of food as it corresponds to energy expenditure. Leptin is a protein created in the white adipose tissue and is comprised of 167 amino acids. The amount of leptin inside the body depends on the amount of fatty tissue. The main purpose of leptin is to react with the receptors in the hypothalamus to control food intake and energy expenditure.
Health Effects and Prevalence of HFCS
High fructose corn syrup is one of the primary sweeteners used in modern foods. Since 1967, utilization of the sugar alternative increased dramatically in a variety of products, most notably soft drinks such as soda and fruit juices. Figures from the U.S. Department of Agriculture show that Americans in the early 21st century consume an average of 132 calories of the product per day. A 2004 article in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition identified a consumption level of over 300 calories in 20 percent of the population.
High fructose corn syrup is a product of cornstarch, combining high levels of glucose and up to 90 percent fructose. The National Center for Biotechnology Information showed in a 1981 report that a high level of fructose raises both blood sugar and insulin in humans. Both of these factors play important roles in the regulation of hunger.
Resistance to Leptin and Danger of High Fructose Corn Syrup
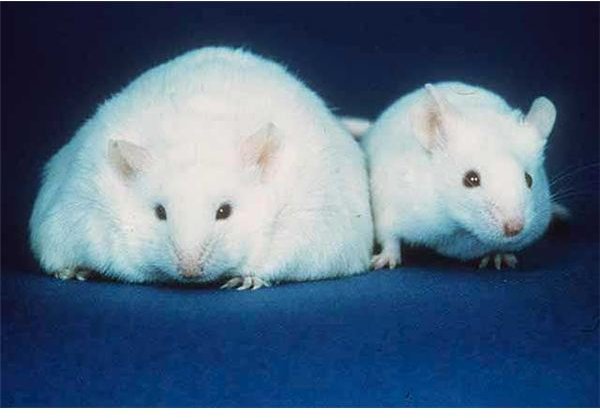
The most important impact on leptin by high fructose corn syrup is the development of a condition known as leptin resistance within the body. When resistance to leptin occurs, the body can no longer respond to the regulatory benefits of the protein.
Researchers from the American Physiological Society showed in 2008 that high levels of fructose can slowly cause leptin regulation to cease functioning properly. Over the course of six months, two different groups of rats were fed high fructose and fructose-free diets. During the time period, no identifiable differences existed between the rats save for one: higher triglyceride levels in the high fructose diet specimens.
At the end of the six months, both sets of rats were injected with additional leptin to see the effects on the animals’ eating levels. Due to the higher level of leptin, the rats should consume less food. However, the rats that consumed high levels of fructose did not lower their food intake levels, while the low-level rats ate less. This means that high levels of fructose creates a situation where normal leptin interaction becomes suppressed within the body. Essentially, too much high fructose corn syrup caused leptin resistance. The rats with this condition ultimately suffered from high levels of weight gain.
This was the first study to demonstrate that leptin resistance can be brought on by high fructose consumption.
Leptin in the Brain
Normally, leptin directly controls the intracellular signaling within the brain by activating signaling cascades. However, when leptin resistance occurs, this is disturbed and transcription factor Stat3 is reduced. A 2008 article in the Journal Endocrinology showed that phosphoinositide 3-kinase, a signaling enzyme, is interrupted, affecting Stat3. In addition, the suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B both appear to inhibit the natural function of leptin.
One identifiable factor that occurs during this process is the elevation of triglycerides in the body. According to the American Physiological Society, triglycerides will impact the blood brain barrier and prevent the transport of leptin from the circulatory system to the cerebrospinal fluid.
This leptin resistance causes the brain to fail to control food intake and can lead to weight gain or obesity. Although the exact connection between the danger of high fructose corn syrup and these enzymes is unknown, the major hypothesis postulates a link.
Additional Resources
Nutrigenomics and the Study of Food Nutrition
Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity
Fructose Sets Table For Weight Gain Without Warning
High fructose corn syrup may leave you hungry..
Leptin resistance and the response to positive energy balance
Image Sources
Soft Drink Shelf. (Supplied by SMC at Wikimedia Commons; Public Domain; https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2a/Soft_drink_shelf.JPG)
Fat mouse. (Supplied by the U.S. Federal Government; Public Domain; https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0b/Fatmouse.jpg)
Blood Brain Barrier. (Supplied by Dan Ferber at Wikimedia Commons; Creative Commons Attribution 2.5; https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/d4/10.1371_journal.pbio.0050169.g001-O.jpg)
